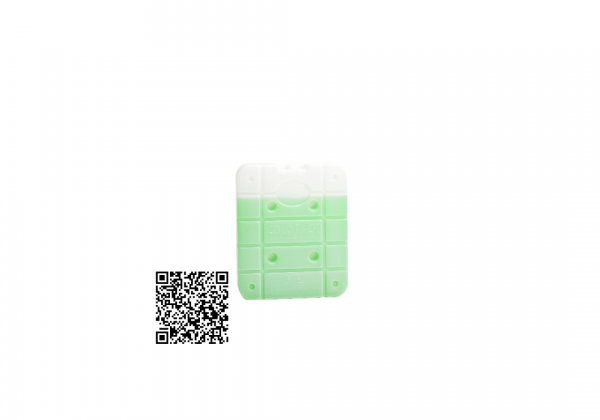
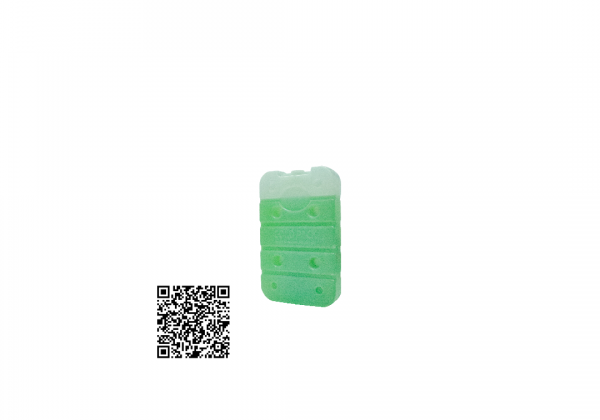
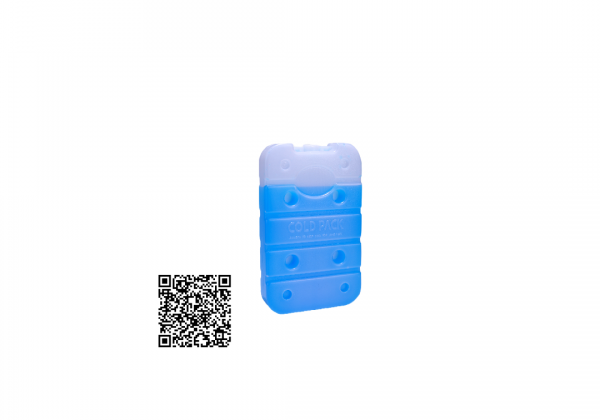
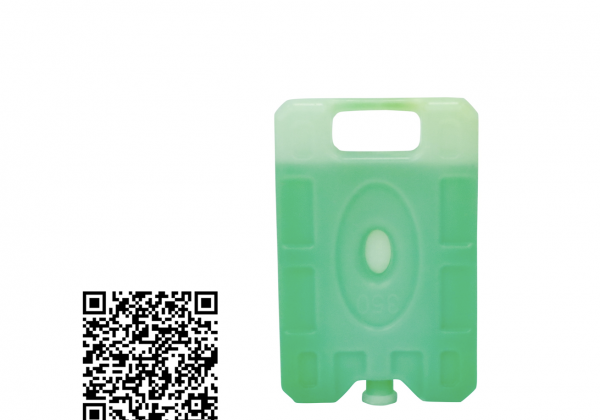
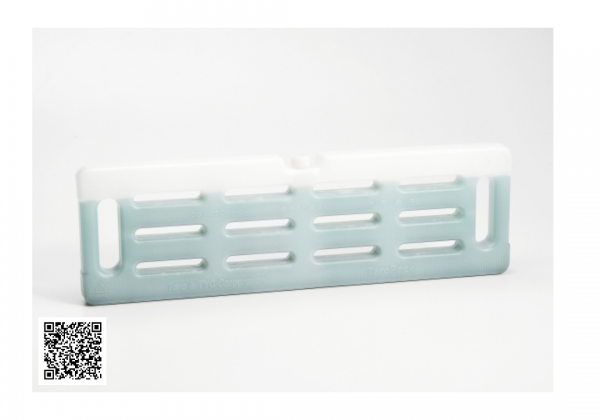
Coolant
- Product Features
- This product uses non-toxic ingredients, but is not edible.
- If the cold preservation agent is damaged or leaked after opening, do not use it.
- The cold preservation agent is made of pure water, is not easy to mold, does not produce odor, and has high safety.
- If the cold air is inadvertently exposed, please treat it with water.
product description
The raw material in the cold-preserving agent has the characteristics of being hard to melt after freezing and having a large heat capacity, and the cooling effect can be extended by more than three times. Safe and non-toxic: the cold preservation agent is made of filtered water, which is not mildewed or smelly. Easy to use: It can be used after freezing and solidification, without the need for additional water, bagging, etc. Reuse: As long as the coolant does not break through, it can be re-used and reused. Wide range of uses: In addition to food cooling applications, it can also be used as ice pillows, ice packs, etc. Note: Please avoid collision and squeeze the cold coolant to avoid leakage.
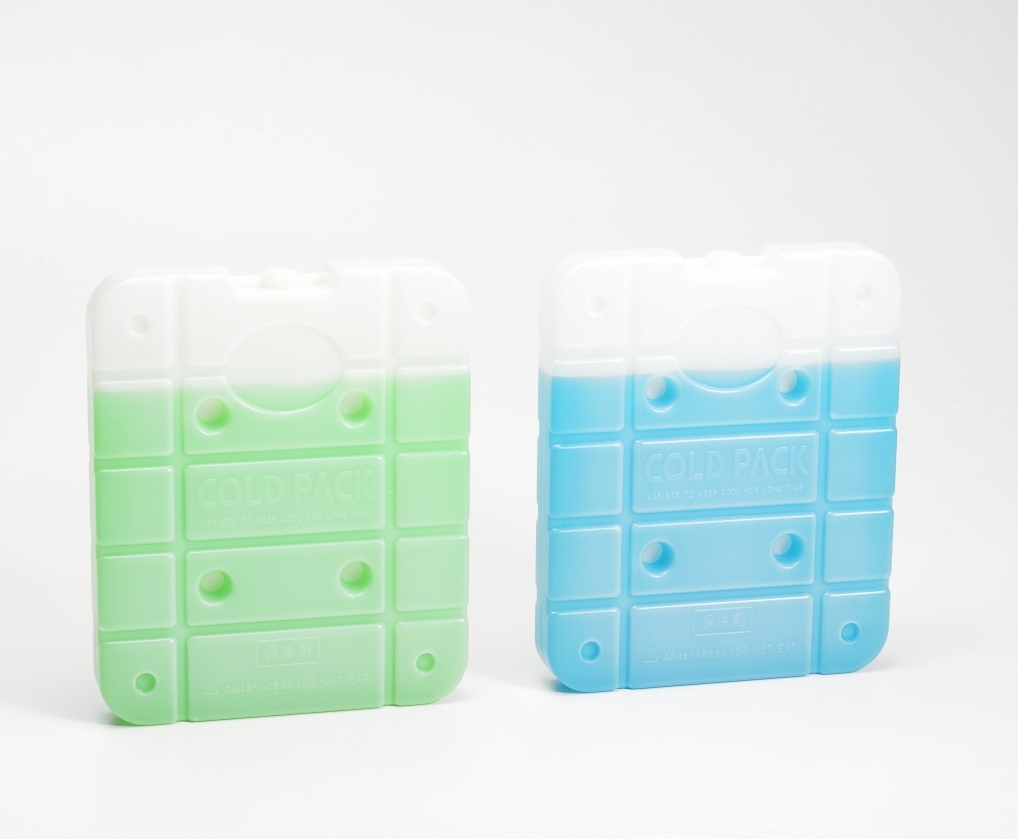

application
There are two kinds of cold preservation agents. The traditional cold preservation agent is made up of high molecular weight polymer (cellulose gel),
and a small part contains edible polypropylene glycol, which is inedible;In the near future, due to the promotion of environmental protection, manufacturers have gradually changed the production of cold-keeping agents composed of water. Up to 98% of the water is environmentally friendly and non-toxic, and can be used repeatedly. It is recommended not to eat.
Common applications include cakes, popsicles and fruit, fresh food preservation, dairy products, and more.
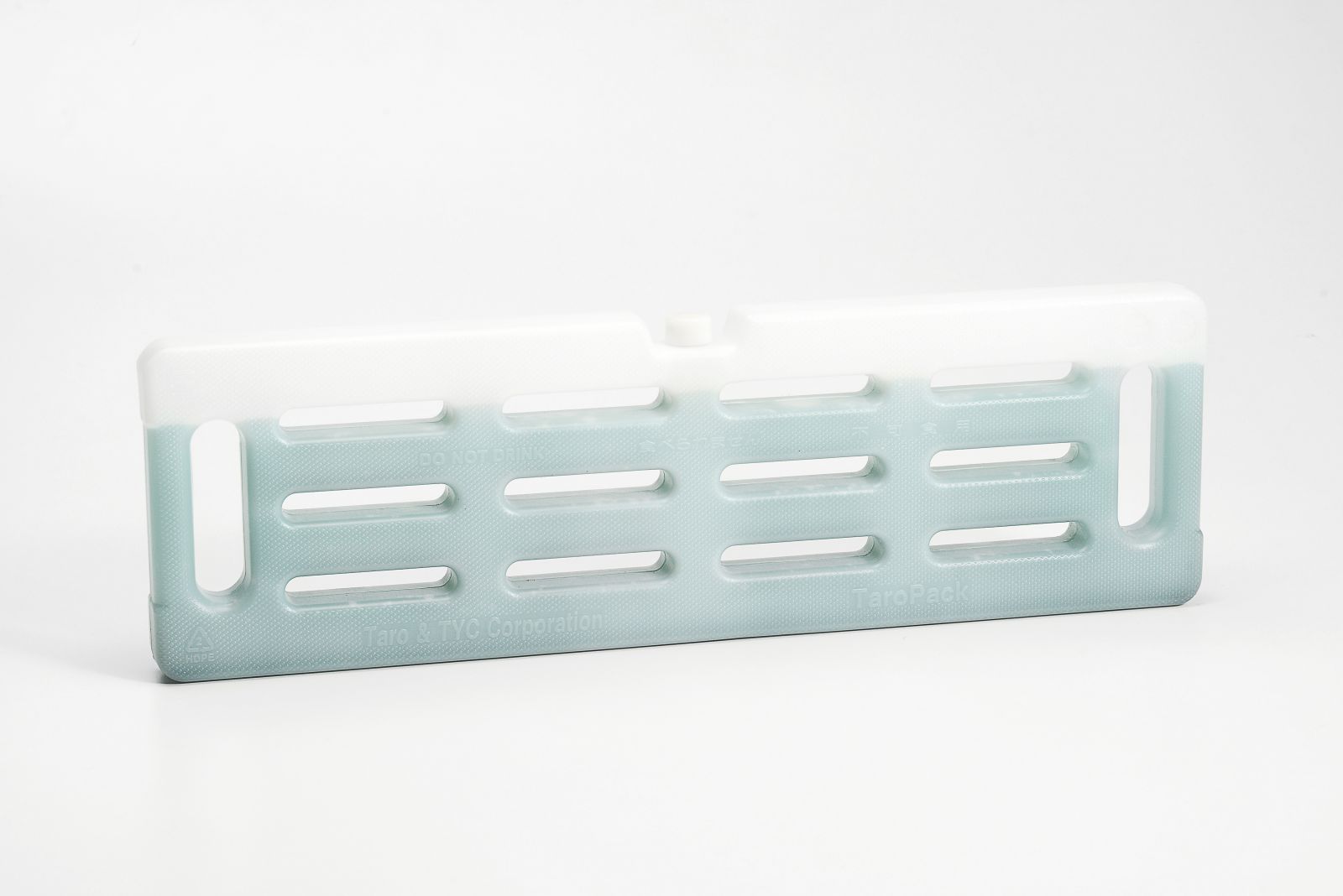
Material
We insist on using high quality virgin material.PP (polypropylene)
Material characteristics
Among the commonly used plastic materials, the density of the PP product is only 0.91 g/cm3, which means that the PP material has the lightest weight in the same volume of the product.
PP has good chemical stability, and its molecules are stable and difficult to dissolve and deform in most acid-base solvents or extreme environments.
Due to the high crystallinity of PP material and the very regular molecular structure, it has excellent mechanical properties, tensile properties and good stress crack resistance, and has a high bending fatigue life.
Excellent heat resistance, PP material processing temperature is about 180-240 degrees Celsius, the chemical composition at high temperatures is still very stable. Under normal use and no external force, it can be used for a long time in an environment of 100 degrees Celsius without deformation.
HDPE (high density polyethylene)
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is made of ethylene. Due to its high crystallinity, high density, strong tensile strength, permeability resistance, and good chemical stability, it is widely used in the production of refrigerator containers. Storage containers, sealing covers, cling film and other products.
Material characteristics
The friction coefficient is low.
Excellent electrical insulation.
Light weight, easy to process, and in direct contact with food.
Excellent toughness and elastic strength are maintained even in low temperature environments.
Excellent chemical stability. At room temperature, it is insoluble in any organic solvent, resistant to acid, alkali and various mites.
Liquid coolant
Heat Transfer Fluid is a more common term used in industrial applications in high or low temperature environments, while coolants are more commonly known in the automotive industry and in HVAC systems. At the same time, because the coolant used in the field of automobiles and HVAC is mainly liquid, it is more often referred to as coolant. In industrial applications, the heat transfer fluid contains both cutting fluids.
The coolant can maintain its original state of matter (eg, gas or liquid) during the cycle, or it can undergo a phase change (change the original state of matter). The presence of latent heat during the phase change makes the coolant more efficient. When a coolant is used to lower the ambient temperature (eg, air conditioner, refrigerator), it is often referred to as a refrigerant.
Liquid coolant
The most common coolant is water. Water has the characteristics of high heat capacity and low price, making it a suitable heat transfer medium. Usually, water is added as an additive such as a corrosion inhibitor and an antifreeze when it is used as a coolant. The antifreeze is a solvent of an organic compound (usually ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, or propylene glycol), and is often used in situations where the water usage environment is below zero or the boiling point needs to be increased. Trimethylamine (also known as betaine) is a similar coolant, but this coolant is made from plants and is therefore non-toxic and easy to handle from an ecological point of view.
Deionized water is often used as a coolant for electrical and electronic equipment, especially high power transmitters and high power vacuum tubes due to its low electrical conductivity.